Other - Diseases
|
Routine Urine Test is an array of tests performed on urine and can be conducted to indicate the presence of a disease or condition. Culture Urine Test is a type of test conducted to diagnose a urinary track infection, as well as to isolated and identify the bacteria or fungus responsible. |
|
Infectious diseases are caused by a microorganism and therefore potentially infinitely transferable to new individuals. Contagious diseases are very communicable disease capable of spreading rapidly from one person to another by contact or close proximity. |
|
Doctors refer to healthcare physicians who practice medicine. There are many different types of doctors depending upon their focus area. Some of the doctors are involved in patient care while some provide support to the work of these doctors. A doctor may also specialize in one or more sub-specialties. |
|
Drug is any substance which alters the normal functioning of the body. Drugs are mainly classified into three main categories – depressants, stimulants and hallucinogens, based on their effect on the central nervous system. |
|
Hemophilia A and Hemophilia are two different types of Hemophilia, caused by the deficiency of coagulation factor VIII and IX respectively. |
|
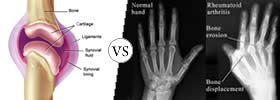
Arthritis is an umbrella term for different disorders and conditions that affect the joints. Rheumatoid Arthritis is an inflammatory type of Arthritis. It is an autoimmune disease and is characterized by severe symptoms like pain, stiffness, loss of appetite and fatigue. |
|
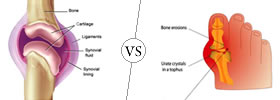
Arthritis is an umbrella term covering more than hundred musculoskeletal disorders. Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis which causes sudden severe attack of pain, swelling and tenderness. |
|
Infection is caused by microorganisms or germs like viruses, protozoa and bacteria. They enter the internal body tissues and then multiply disrupting the normal functionality of the cell. On the other hand, infestation refers to the inflection by larger and complex organisms than germs especially arthropods which reproduce on the exterior surfaces of the body. The term infestation is also used to describe the invasion of the gastrointestinal tract by parasitic worms. |
|
An infection is a phenomenon which is caused by invasion of microorganisms or germs into the body. It can be limited to a body region or can be widespread. Sepsis is the body’s response to an infection. It is generally associated with inflammatory response and eventually organ dysfunction and/or failure. Thus, if an infection is left untreated or not treated properly then an infection can often progress to sepsis. |
|
Snoring is the hoarse sound that is caused by partial obstruction of breath in some way while sleeping, whereas ‘sleep apnea’ is caused by the temporary stoppage or suspension of breath for few seconds due to the complete obstruction of air passage. Snoring is an abnormal sound whereas apnea is a sleep disorder. |
|
Flu is a contagious respiratory illness caused by an RNA virus from the family known as orthomyxoviridae. It affects birds and mammals. On the other hand, Bird Flu is caused by influenza Type viruses. It infects birds and sometimes it can be transmitted to humans too. |
|
Hypothyroidism is a condition which arises from insufficient production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland. Cretinism is a condition arising from the deficiency of thyroid hormone, which causes dwarfism and mental retardation. It is present from birth. |
|
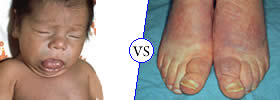
Cretinism is a condition arising from the deficiency of a thyroid hormone, which is characterized by dwarfism and mental retardation. Goitre is a swelling caused in the thyroid gland by under or over production of hormones by the gland. |
|
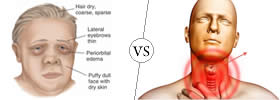
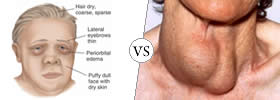
Myxedema is a disease resulting from the under-activity of the thyroid gland, which is characterized by puffy eyes, face, hands and mental sluggishness. Cretinism is a condition arising from a deficiency of thyroid hormone, which is characterized by dwarfism and mental retardation. |
|
Dwarfism is defined as the condition of being a dwarf. Achondroplasia is a skeletal disorder, which is characterized by the failure of normal conversion of cartilage into bone that begins during fetal life and causes dwarfism. |
Pages
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |