Difference between Wet Cell and Dry Cell Battery
Key Difference: Wet Cell batteries predate dry cells. The primary difference between a wet cell and dry cell battery is that the wet cell battery uses a liquid electrolyte, whereas a dry cell uses a paste electrolyte.
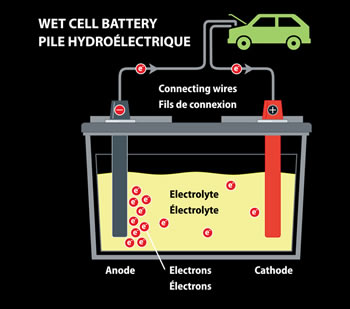 A battery is a useful item and these days is a necessary one too. Nearly all devices either run directly on electricity or use a battery to store electricity, which allows the device to function while also allowing it portability, i.e. it is able to move from one place to another without being connected to a power supply. There are many different types of batteries, two of the most common categories of batteries are wet cell battery and dry cell battery. See AA Battery Vs. AAA Battery.
A battery is a useful item and these days is a necessary one too. Nearly all devices either run directly on electricity or use a battery to store electricity, which allows the device to function while also allowing it portability, i.e. it is able to move from one place to another without being connected to a power supply. There are many different types of batteries, two of the most common categories of batteries are wet cell battery and dry cell battery. See AA Battery Vs. AAA Battery.
Wet Cell batteries, also known as “flooded battery,” predate dry cells. They were primarily used before dry cell batteries became effective and more popular. While, wet cell batteries are still used today they are less common than dry cell batteries, which are used for nearly everything now, from smartphones and other electronic devices to regular household items such as flashlights and clocks.
The primary difference between a wet cell and dry cell battery is that the wet cell battery uses a liquid electrolyte, whereas a dry cell uses a paste electrolyte. The electrolyte is what allows the battery to transfer a charge between nodes. Due to the usage of a liquid electrolyte, the wet cell battery must be used in a specific orientation, i.e. the right side up, using the battery in any other way will result in the spilling of the liquid electrolyte. The dry cell does not have this problem and can typically be used in any direction. Also see: Capacitor Vs.Battery
Wet Cell Batteries are usually larger in capacity and carry a larger charge. Hence, they are commonly used for larger items such as in automobiles, aviation, electric utilities, cellphone towers, and for energy storage. Dry Cell Batteries, on the other hand, are usually smaller and carry a lesser charge. Hence, they are typically used for smaller devices such as clocks, toys, cell phone, laptops, and other such portable devices.
As wet cell batteries are typically larger in size they cannot easily be moved around. Some of the larger batteries may be even more difficult to move. Whereas, the dry cell battery is typically smaller in size and can be moved around easily. Hence, it can be said that the dry cell batteries have a more range of motion than wet cell batteries. It is also because of this that devices that use dry cell battery are often portable, whereas those using wet cell batteries usually aren’t.
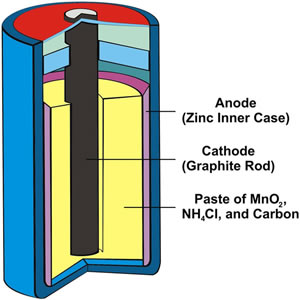 An additional challenge of moving the wet cell battery is that the liquid electrolyte might spill, and the electrolytes are typically a highly corrosive liquid substance such as sulfuric acid which will cause damage to anything it comes into contact with. Hence, one has to be extra careful while transporting or moving a wet cell battery. See: Battery Vs. Rechargeable battery
An additional challenge of moving the wet cell battery is that the liquid electrolyte might spill, and the electrolytes are typically a highly corrosive liquid substance such as sulfuric acid which will cause damage to anything it comes into contact with. Hence, one has to be extra careful while transporting or moving a wet cell battery. See: Battery Vs. Rechargeable battery
Both wet cell and dry cell battery come in rechargeable and non-rechargeable types. The non-rechargeable batteries are to be used once and then thrown away or recycled, whereas rechargeable batteries can be recharged again and again for use.
The dry cell batteries are more common and popular today than the wet cell batteries. They are surely and quickly replacing wet cell batteries are they provide certain benefits over the wet cell batteries, such as they are safer and easier to use, while also being highly portable.
Difference between Wet Cell and Dry Cell Battery:
|
|
Wet Cell Battery |
Dry Cell Battery |
|
Description |
A wet cell battery has a liquid electrolyte. Other names are flooded cell since the liquid covers all internal parts, or vented cell since gases produced during operation can escape to the air. |
A Dry cell is a type of electricity-producing chemical cell, commonly used today for many home and portable devices, often in the form of batteries. It uses a paste electrolyte. |
|
Age |
Older in comparison |
Newer in comparison |
|
Electrolyte |
Liquid electrolyte |
Paste electrolyte |
|
Directional Usage |
Typically can be used only in one direction. Usage in other orientation may result in spilling. |
Can operate in any orientation without spilling |
|
Gases |
Can produce gases that are harmful to health. |
Typically does not produce gases. |
|
Movability |
Limited or difficult |
Easy and portable |
Reference: Wikipedia, Call to Recycle, UPS Battery Center (Dry and Wet) Image Courtesy: upsbatterycenter.com







Add new comment