Difference between Animal and Mammal
Key difference: All mammals are animals, but all animals are not mammals. The drastic feature which separates a mammal from an animal is that mammals have mammary glands, which all animals do not have.
The word “animal” comes from the Latin word animalis, meaning “having breath”. They belong to the kingdom Animalia. Biologically, the word is defined as ‘all members of the kingdom Animalia, encompassing creatures as diverse as sponges, jellyfish, insects, and humans’.
 Animals are multi-cellular, eukaryotic organisms of the kingdom Animalia or Metazoa. They comprise of a wide spectrum of species and different categories of animals. They are terrestrial, aquatic, aerial and amphibious in habitats. Their body structure is eventually fixed as they develop and undergo a process of metamorphosis in their lives. They are motile, that is they can move spontaneously and independently. Animals are divided into various sub-groups, including birds, mammals, amphibians, reptiles, fish and insects.
Animals are multi-cellular, eukaryotic organisms of the kingdom Animalia or Metazoa. They comprise of a wide spectrum of species and different categories of animals. They are terrestrial, aquatic, aerial and amphibious in habitats. Their body structure is eventually fixed as they develop and undergo a process of metamorphosis in their lives. They are motile, that is they can move spontaneously and independently. Animals are divided into various sub-groups, including birds, mammals, amphibians, reptiles, fish and insects.
Animals have numerous characteristics which distinguishes them from living-beings. They are eukaryotic and multicellular, which separates them from bacteria and most protists. They are heterotrophic in nature and digest the food in an internal chamber. They also lack rigid cell walls, these feature separates them from plants and algae. Their structure ranges from the tissue type of sponges (Phylum Porifera) and Placozoa, till the fully matured grown type of muscles and the nervous system of humans. Their formation includes many chemicals comprising of hormones, proteins, genes, bones, etc. They obtain the energy from the source of food, which provides them with all the essential and nutritive components necessary for growth. The type of food depends on the type of category of the animals.
Animals reproduce sexually as well as asexually. Nearly all animals undergo some form of sexual reproduction. They have a few specialized reproductive cells, which undergo meiosis to produce smaller, motile spermatozoa or larger, non-motile ova. These fuse to form zygotes, which develop into a new individual. Many animals also reproduce asexually. This takes place through parthenogenesis, where fertile eggs are produced without mating, budding, or fragmentation.
The word “mammal”, is originated from the scientific name Mammalia coined by Carl Linnaeus in 1758, derived from the Latin mamma. They are divided into two subclasses (not counting fossils):
- The Prototheria (order of Monotremata) and
- The Theria. (Composed of the infraclasses Metatheria and Eutheria).
The marsupials comprise the crown group of the Metatheria, which includes all living metatherians, as well as many extinct ones. The placentals constitute the crown group of the Eutheria.
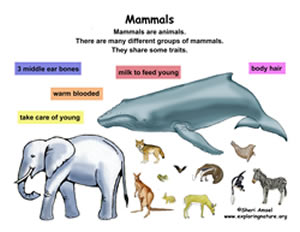
Mammals (class Mammalia ) are a clade of endothermic amniotes. They include the largest animals on the planet comprising of the rorqual whales, elephants (intelligent of all animals) and some primates and some cetaceans. Mammals are warm blooded animals and have a closed circularity system with a sophisticated four-chambered heart. The features that distinguish them from other amniotes are the reptiles and birds which have hair and three middle ear bones. In females, there are mammary glands, and a neocortex (a region of the brain). The mammalian brain regulates the body temperature and the circulatory system, including the four-chambered heart. They have a basic body type of the four-legged land-born animal. Some also with two legs adapted to sea, air and trees.
The anatomy and morphology of mammals includes the system such as:
- Skeletal system
- Respiratory system
- Nervous system
- Integumentary system
- Reproductive system
The reproduction systems of mammals are of at most importance. Most mammals are viviparous, that is they give birth to young ones. However, the five species of the monotreme, platypuses and echidnas lay eggs. The monotremes have a sex determination system, which is different from most other mammals. In particular, the sex chromosomes of a platypus are more like those of a chicken than those of a therian mammal.
Comparison between Animals and Mammals:
|
|
Animals |
Mammals |
|
Belongs to |
They belong to kingdom Animalia or Metazoa |
They belong to kingdom Animalia. |
|
Conversions |
All animals cannot be mammals. |
All mammals are animals. |
|
Categories |
They comprises of all ranges of animals. |
They are categorized to only those animals, which have mammary glands. |
|
Comprises of |
They are oviparous as well as viviparous. |
They are viviparous only. |
|
Types |
They are both endothermic as well as exothermic. |
They are only endothermic animals. |
|
Typical features |
They comprise of all the featured types of animals. |
They have a typical feature of having hair on the skin. |
|
Habits |
They have less complex habits compared to mammals. |
They have more complex living habits. |
|
Count |
They are in large number compared to the mammals. |
They are a fraction of the animals. |
|
Heart features |
They comprises of heart ranging from single cellular organisms to the multi-cellular humans. |
Most sophisticated heart and circulatory system are present in mammals. |
|
Examples |
Birds, reptiles, aquatic animals like whales, fish, etc., carnivorous, herbivorous, micro-organisms and many. |
Humans, elephants, tiger, lion, etc. |
Image Courtesy: pkwy.k12.mo.us, exploringnature.org








Add new comment