Difference between 4G and LTE
Key difference: LTE is faster than what is traditionally marketed as 4G. In that regard, it is also usually more expensive. 4G in turn is faster than 3G.
 These days smartphones are a must. If one does not have a smartphone then they run the risk of missing out. FOMO, i.e. fear of missing out commands us to not only get a smartphone, but a data plan as well. After all, what good is a smartphone if you cannot use it to constantly keep in touch with social media.
These days smartphones are a must. If one does not have a smartphone then they run the risk of missing out. FOMO, i.e. fear of missing out commands us to not only get a smartphone, but a data plan as well. After all, what good is a smartphone if you cannot use it to constantly keep in touch with social media.
However, these are not easy decisions to make, especially if you are not technologically gifted, which most of us are not. The first decision you are faced with whether or not to get a smartphone. If you are even remotely living in today’s world, then yes you do. Then comes the question of which phone to get. Let’s for the sake of argument assume that you already have one. Yet the decisions don’t end there. Then you have to decide which data plan to get. Are you still stuck on 2G? The least you need is 3G. Should you upgrade to 4G? And what is LTE?
Believe it or not, all of these are types of data plans you can get. The most basic difference between 2G, 3G, and 4G, especially from a layman’s point of view is the speed of the internet. However, what is LTE? And as if deciding between them wasn’t hard enough, you also have to ensure that you phone is compatible with it.
The first time anyone could access anything on their phone was with a 2G network. However, this network was quite slow and was only meant for small data packets, which could be transferred on the limited network.
After 2G, came the 3G. Now 3G is the basic network that is considered the minimum to have. However, this network is not that fast either. It is faster than 2G, but the network is still incapable of handling large data packets. Due to this, many websites have to rendered especially with low data so as to be able to load on a 3G network.
This is where 4G comes into play. 4G stands for the 4th generation of telecommunication standard as set by The International Telecommunication Union (ITU), a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN). As per their guidelines, 4G networks should have a 100 megabits per second (Mbit/s) for high mobility communication, such as from trains and cars, and 1 gigabit per second (Gbit/s) for low mobility communication, such as pedestrians and stationary users. However, as anybody can tell you, the current 4G speeds are nowhere close to that.
In reality, any speed that was an improvement over the speed of 3G is labeled as 4G. The truth of the matter is that the term 4G is less like a technical specification, and more like marketing term. When the ITU announced the speed limits of 4G, they intended them to be a target for telecommunications to hit. Even today, the speeds are not that close to the specified limitations, but they are certainly closer; and the gap is closing faster every day.
This is where LTE comes in. LTE stands for Long Term Evolution. It indicates that the technologies are on their way to meet up with 4G specifications, as they have been specified by the ITU. LTE is a term that can use utilized for technologies that are not the ideal 4G yet, but are using every technology possible to get there. Yet, the term can only be used if the speeds of the network are significantly better than 3G.
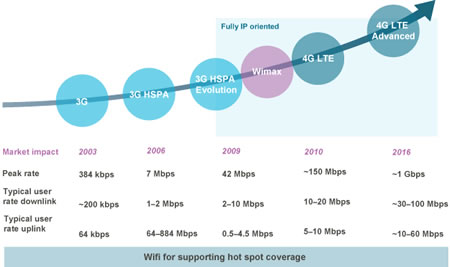 So, in conclusion what does that mean for your data plan? In short, LTE is faster than what is traditionally marketed as 4G. In that regard, it is also usually more expensive. Another thing to note is that in order to harness the speeds of LTE, the phone or device should be LTE enabled, which means it should have the corresponding adaptors and other technologies, otherwise you will not get the speed of the LTE. You will instead get the speed of whatever technology that phone is capable of harnessing.
So, in conclusion what does that mean for your data plan? In short, LTE is faster than what is traditionally marketed as 4G. In that regard, it is also usually more expensive. Another thing to note is that in order to harness the speeds of LTE, the phone or device should be LTE enabled, which means it should have the corresponding adaptors and other technologies, otherwise you will not get the speed of the LTE. You will instead get the speed of whatever technology that phone is capable of harnessing.
Another thing that affects speed is location and network. Speed varies from service provider to service provider. It depends on the company, and how good their network is. The speeds in metropolitan areas are usually higher than in suburban or rural areas, where at times the speeds are even lower than 3G. So, keep these factors in mind, before purchasing a LTE enabled phone or data plan.
Comparison between 4G and LTE:
|
|
4G |
LTE |
|
Stands for |
4th Generation |
Long Term Evolution |
|
Description |
4th generation of telecommunication standard as set by The International Telecommunication Union (ITU), a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN). |
Indicates that the technologies are on their way to meet up with 4G specifications. |
|
Ideal Data Speed |
100 megabits per second (Mbit/s) for high mobility communication, such as from trains and cars, and 1 gigabit per second (Gbit/s) for low mobility communication, such as pedestrians and stationary users |
|
|
Actual Data Speed |
Varies according to country and region, as well as network provider |
Varies according to country and region, as well as network provider |
|
Relative Data Speed |
Faster than 3G, but nowhere close to actual 4G |
Faster that marketed 4G, but nowhere close to actual 4G |
Reference: Wikipedia (4G and LTE), Digital Trends, NYTimes, iAnswerGuy Image Courtesy: androidagent.com, androidauthority.net









Comments
Abhishek.
Wed, 10/26/2016 - 13:22
Add new comment