Difference between LCD and LED Televisions
Key Difference: LCDs are type of television screens that use liquid crystals sandwiched between two sheets of polarizing material. LED (Light emitting diode) TVs are still LCD TVs that replace the original LCD’s CCFL (Cold Cathode Fluorescent Lamp) technology with LED technology. An LED TV’s screen is also made up of liquid crystals.
LED TVs have become a new trend, an upgrade to LCDs if you must. Companies have been labeling the LED TVs as new technology, which is not true. LCDs and LEDs have a lot in common. Let’s look at the definition of an LCD first.
 An LCD is type of television screen that uses liquid crystals sandwiched between two sheets of polarizing material. LCDs provide significant benefits compared to CRTs and plasmas, such as they consume less power than both. Both CRTs and Plasmas are susceptible to burn-ins while LCDs are not. LCDs are also best to display in small sizes, anything bigger than 40 inches becomes expensive compared to plasmas. It also faces a dead pixel problem, where pixels can die causing a spot to appear on the screen. However, LCDs require a backlight as it cannot emit light. This is the major difference between an LCD and a LED, while LCDs require a backlight; LEDs can emit light by themselves.
An LCD is type of television screen that uses liquid crystals sandwiched between two sheets of polarizing material. LCDs provide significant benefits compared to CRTs and plasmas, such as they consume less power than both. Both CRTs and Plasmas are susceptible to burn-ins while LCDs are not. LCDs are also best to display in small sizes, anything bigger than 40 inches becomes expensive compared to plasmas. It also faces a dead pixel problem, where pixels can die causing a spot to appear on the screen. However, LCDs require a backlight as it cannot emit light. This is the major difference between an LCD and a LED, while LCDs require a backlight; LEDs can emit light by themselves.
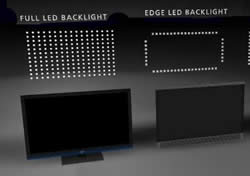 LED (Light emitting diode) TVs are still LCD TVs that replace the original LCD’s CCFL (Cold Cathode Fluorescent Lamp) technology with LED technology. An LED TV’s screen is also made up of liquid crystals. A LED is a semiconductor device and when it is switched on, electrons are able to recombine with electron holes within the device and release energy in form photons or light. This light emitted from an LED is used as a backlighting for an LCD TV. There are two forms in which and LED is used to light up an LCD; edge lighting and full array lighting.
LED (Light emitting diode) TVs are still LCD TVs that replace the original LCD’s CCFL (Cold Cathode Fluorescent Lamp) technology with LED technology. An LED TV’s screen is also made up of liquid crystals. A LED is a semiconductor device and when it is switched on, electrons are able to recombine with electron holes within the device and release energy in form photons or light. This light emitted from an LED is used as a backlighting for an LCD TV. There are two forms in which and LED is used to light up an LCD; edge lighting and full array lighting.
In edge lighting, a series of diodes are arranged along the outside edges of the screen, when a current is applied the light is then distributed evenly along the screen. This is similar to using CCFL lighting as it does not have local-dimming capabilities (where images are dimmed in response to their surroundings). In fully-array, the diodes are spread across the entire surface of the screen. These are faster in response and include the local-dimming feature as they have the capability of turning on and off independently.
As you can see a better term for a LED TV would be LED-backlit LCD TV. A few benefits that an LED backlight provides is that it extends the life span of the TV, provides a better image, has the ability to provide Jet black level, and is thinner and lighter compared to the CCFL LCDs. These are however more expensive compared to the original LCDs.
|
|
LCD |
LED |
|
Thickness |
Thicker compared to LED |
Thinner compared to LCD |
|
Power consumption |
Consumes more power compared to LED |
Consumes less power than LCD |
|
Screen Refresh Rate |
Less than LED |
Greater than LED |
|
Screen glare |
Glare is minimum |
Glare is minimum |
|
Running Temperature |
Cool |
Cool |
|
Burn-in |
No burn-in occurs; but burn-outs can occur |
No burn-in occurs; but burn-outs can occur |
|
Dead pixels |
Can occur |
Can occur |
|
Viewing angle |
Up to 165 degrees |
Up to 165 degrees |
|
Contrast Ratio |
15000:1 |
15000:1 |
|
Life span |
60,000 hours |
100,000 hours |
|
Black level |
Gray to Dark Gray |
Jet Black |
|
Weight |
Heavier compared to LED |
Lighter compared to LCD |
|
Uses |
Computer monitors, laptop screens, TV screens and cell phone screens |
Computer monitors, laptop screens, TV screens and cell phone screens |
|
Price |
Cheaper |
More expensive |
|
Benefits |
Panels weigh less than plasma; use less energy; light; thinner; emits less electromagnetic radiation; no bleeding or smearing |
Weight less than LCD; have a longer life; more environment friendly; lower power consumption; more reliable |
|
Limitations |
Slower refresh rate; limited viewing angle; blacks are brighter; susceptible to burn-out and image persistence; dead or stuck pixels may appear; smearing or ghosting can appear; loss of contrast in higher temperatures; poor display in sunlight |
Expensive |
Image Courtesy: televisions.com, ledvslcd.com









Add new comment