Difference between Class and Structure in C++
Key Difference: C++ is an object oriented language that mainly focuses on objects. A class in C++ can be defined as a collection of related variables and functions encapsulated in a single structure. Instances of the class are termed as objects. A structure in C++ can be referred to as an user defined data type possessing its own operations. Unlike in the C language, they both are quite similar in C++. The main difference that exists between them is regarding the access modifier; the members of a class are private by default, whereas members of a struct are public by default.

A class in C++ is just an extension of a structure used in the C language. It is a user defined data type. It actually binds the data and its related functions in one unit. A structure and a class in C language differs a lot as a structure has limited functionality and features as compared to a class. On the other hand, structure and class in C++ are quite similar. The main difference arises due to the fact that by default, all the members of a class are private, whereas by default all the members of a structure are public.
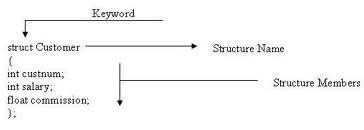
Comparison between Class and Structure in C++:
|
|
Class |
Structure |
|
Definition |
A class in C++ can be defined as a collection of related variables and functions encapsulated in a single structure. |
A structure can be referred to as a user defined data type possessing its own operations. |
|
Keyword for the declaration |
Class |
Struct |
|
Default access specifier |
Private |
Public |
|
Example |
class myclass { private: int data; public: myclass(int data_): data(data_) {} virtual void foo()=0; virtual ~class() {} }; |
struct myclass { private: int data; public: myclass(int data_): data(data_) {} virtual void foo()=0; virtual ~class() {} }; |
|
Purpose |
Data abstraction and further inheritance |
Generally, grouping of data |
|
Type |
Reference |
Value |
|
Usage |
Generally used for large amounts of data. |
Generally used for smaller amounts of data. |
Image Courtesy: tapkaa.com, exforsys.com







Add new comment