Difference between Cardiac Arrest and Stroke
Key Difference: Cardiac Arrest is a heart condition where the heart does not contract properly, thereby failing to effectively circulate blood to the other organs. Cardiac arrest is brought on by irregular beating of the heart that causes it to stop supplying blood flow to the other organs, including the brain. Stroke is the loss of brain function due to blockage of blood to the brain. The brain requires oxygenated blood and nutrients from the heart. When the brain fails to receive the blood, it stops functioning and the brain cells start dying. A stroke can be referred to as a “brain attack”.
Cardiac arrest and stroke are two different medical conditions that affect different parts of the body. Cardiac arrest deals with the heart, while stroke deals with the brain. Because of the medical lingo, many people often become confused between the different medical conditions. Cardiac arrest is when the heart is unable to pump blood to the rest of the organs. Stroke deals with the inability of the brain to receive blood due to a blockage or burst vein in the brain.
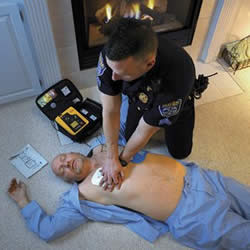 Cardiac Arrest is a heart condition where the heart does not contract properly, thereby failing to effectively circulate blood to the other organs. Cardiac arrest is brought on by irregular beating of the heart that causes it to stop supplying blood flow to the other organs, including the brain. Cardiac arrest is also known as cardiopulmonary arrest or circulatory arrest. The heart has an internal electrical system that allows it to control the rhythm of the heart; any changes to the rhythm can cause the heart to either beat too fast, too slow or stop beating completely. These changes are known as arrhythmias. The lack of blood flow leaves the other organs starved for oxygenated blood. The lack of oxygen to the brain causes the person to faint. If the person does not receive help during the first five minutes of fainting, it can result in permanent damage to the brain.
Cardiac Arrest is a heart condition where the heart does not contract properly, thereby failing to effectively circulate blood to the other organs. Cardiac arrest is brought on by irregular beating of the heart that causes it to stop supplying blood flow to the other organs, including the brain. Cardiac arrest is also known as cardiopulmonary arrest or circulatory arrest. The heart has an internal electrical system that allows it to control the rhythm of the heart; any changes to the rhythm can cause the heart to either beat too fast, too slow or stop beating completely. These changes are known as arrhythmias. The lack of blood flow leaves the other organs starved for oxygenated blood. The lack of oxygen to the brain causes the person to faint. If the person does not receive help during the first five minutes of fainting, it can result in permanent damage to the brain.
Cardiac arrest can be a cause of Coronary heart disease, cardiac abnormalities such as cardiomyopathy, cardiac rhythm disturbances, hypertensive heart disease, congestive heart failure, etc., trauma, overdose, drowning, smoking, obesity, lack of physical exercise, etc. Cardiac arrest brought on suddenly is known as Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA) and causes the heart to stop beating completely. Cardiac arrest differs from heart attack as in a heart attack, the heart does not receive the oxygenated blood and all the while it continues to beat and pump until the cells die completely. In cardiac arrest, the heart itself stops beating, though it still receives constant supply of oxygenated blood.
Symptoms of cardiac arrest include fainting and loss of pulse or heartbeat. The person stops breathing as the heart no longer pumps. The person that suffers a cardiac arrest must receive quick cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) to keep the heart pumping the brain from losing cells. The longer it takes the person to receive help, the more chances that they may have loss of memory, brain damages or less chances of survival. Defibrillation (or shocking the heart) is another way to revive the heart. Implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) and pacemakers are used to ensure that the person does not suffer from another cardiac arrest episode in the event of arrhythmia.
 Stroke is the loss of brain function due to blockage of blood to the brain. The brain requires oxygenated blood and nutrients from the heart. When the brain fails to receive the blood, it stops functioning and the brain cells start dying. A stroke can be referred to as a “brain attack”. This is similar to a heart attack, but this blocking of blood flow occurs in the brain and not in the heart. This occurs in almost the same manner, causing blood to stop flowing to a certain part of the brain and the brain cells start to die, leaving a permanent damage.
Stroke is the loss of brain function due to blockage of blood to the brain. The brain requires oxygenated blood and nutrients from the heart. When the brain fails to receive the blood, it stops functioning and the brain cells start dying. A stroke can be referred to as a “brain attack”. This is similar to a heart attack, but this blocking of blood flow occurs in the brain and not in the heart. This occurs in almost the same manner, causing blood to stop flowing to a certain part of the brain and the brain cells start to die, leaving a permanent damage.
There are two types of strokes: an ischemic stroke or a hemorrhagic stroke. An ischemic stroke occurs when a clot is either formed or breaks off from another place and travels to the brain blocking the blood flowing to the brain. A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel in a part of the brain becomes weak and bursts causing blood to leak in the brain. Time plays an important factor in the recovery of the patient, as more time pass more irreversible damage is done to the brain. Recovery from damage ideally includes therapy such as memory therapy, speech therapy, physical therapy, etc.
Symptoms of stroke include: Severe headache, loss of balance, numbness, loss of movement in one side, double vision or loss of vision, loss of speech or memory and an altered breathing or heart rate. There is a procedure created known as FAST that helps determine if a person is suffering from a stroke. FAST is an anagram for Face, Arm, Speech and Time. Face states that is the patient’s face drooping or ask them to smile to see if they can perform the function. Arm states to ask the person to hold out their arms in front of them straight, determine if they are able to fulfill the activity. Speech – is the person’s speech slurred? Ask them to repeat a sentence. The time states if the person is unable to perform any of the functions above, the person should call medical professionals.
Image Courtesy: ece.uc.edu, whitetigernaturalmedicine.com








Add new comment