Difference between Cardiac Arrest and Respiratory Arrest
Key Difference: Cardiac Arrest is a heart condition where the heart does not contract properly, thereby failing to effectively circulate blood to the other organs. Cardiac arrest is brought on by irregular beating of the heart that causes it to stop supplying blood flow to the other organs, including the brain. Respiratory arrest is the condition when a person stops breathing as their lungs fail to contract effectively. It prevents the body from delivering oxygen to the body, including the brain causing the person to lose consciousness.
Cardiac arrest and respiratory breathing are two conditions that are quite similar to each other as they both cause the patient to lose consciousness. This causes many people to confuse the two medical emergencies, but these are two distinct conditions and should be treated as such. Cardiac arrest and respiratory arrest go hand-in-hand, with one either causing or is caused by the other. Cardiac arrest is when the heart does not contract properly resulting in loss of oxygenated blood throughout the body. Respiratory arrest is when a person stops breathing causing lack of oxygen in the brain.
 Cardiac Arrest is a heart condition where the heart does not contract properly, thereby failing to effectively circulate blood to the other organs. Cardiac arrest is brought on by irregular beating of the heart that causes it to stop supplying blood flow to the other organs, including the brain. Cardiac arrest is also known as cardiopulmonary arrest or circulatory arrest. The heart has an internal electrical system that allows it to control the rhythm of the heart; any changes to the rhythm can cause the heart to either beat too fast, too slow or stop beating completely. These changes are known as arrhythmias. The lack of blood flow leaves the other organs starved for oxygenated blood. The lack of oxygen to the brain causes the person to faint. If the person does not receive help during the first five minutes of fainting, it can result in permanent damage to the brain.
Cardiac Arrest is a heart condition where the heart does not contract properly, thereby failing to effectively circulate blood to the other organs. Cardiac arrest is brought on by irregular beating of the heart that causes it to stop supplying blood flow to the other organs, including the brain. Cardiac arrest is also known as cardiopulmonary arrest or circulatory arrest. The heart has an internal electrical system that allows it to control the rhythm of the heart; any changes to the rhythm can cause the heart to either beat too fast, too slow or stop beating completely. These changes are known as arrhythmias. The lack of blood flow leaves the other organs starved for oxygenated blood. The lack of oxygen to the brain causes the person to faint. If the person does not receive help during the first five minutes of fainting, it can result in permanent damage to the brain.
Cardiac arrest can be a cause of Coronary heart disease, cardiac abnormalities such as cardiomyopathy, cardiac rhythm disturbances, hypertensive heart disease, congestive heart failure, etc., trauma, overdose, drowning, smoking, obesity, lack of physical exercise, etc. Cardiac arrest brought on suddenly is known as Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA) and causes the heart to stop beating completely. Cardiac arrest differs from heart attack as in a heart attack, the heart does not receive the oxygenated blood and all the while it continues to beat and pump until the cells die completely. In cardiac arrest, the heart itself stops beating, though it still receives constant supply of oxygenated blood.
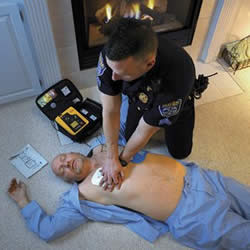
Symptoms of cardiac arrest include fainting and loss of pulse or heartbeat. The person stops breathing as the heart no longer pumps. The person that suffers a cardiac arrest must receive quick cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) to keep the heart pumping the brain from losing cells. The longer it takes the person to receive help, the more chances that they may have loss of memory, brain damages or less chances of survival. Defibrillation (or shocking the heart) is another way to revive the heart. Implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) and pacemakers are used to ensure that the person does not suffer from another cardiac arrest episode in the event of arrhythmia.
 Respiratory arrest is the condition when a person stops breathing as their lungs fail to contract effectively. It prevents the body from delivering oxygen to the body, including the brain causing the person to lose consciousness. Following respiratory arrest can be caused by or can cause cardiac arrest. The person can go into cardiac arrest within minutes of respiratory arrest. If the person does not receive medical help or assisted breathing in five minutes from the moment they went into respiratory arrest, the person may suffer permanent brain damage. The moment the brain stops receiving oxygen, cells start to die of asphyxiation. This can cause memory loss, paralysis, or any other type of permanent, irreversible damage.
Respiratory arrest is the condition when a person stops breathing as their lungs fail to contract effectively. It prevents the body from delivering oxygen to the body, including the brain causing the person to lose consciousness. Following respiratory arrest can be caused by or can cause cardiac arrest. The person can go into cardiac arrest within minutes of respiratory arrest. If the person does not receive medical help or assisted breathing in five minutes from the moment they went into respiratory arrest, the person may suffer permanent brain damage. The moment the brain stops receiving oxygen, cells start to die of asphyxiation. This can cause memory loss, paralysis, or any other type of permanent, irreversible damage.
Respiratory arrest can be caused by various different factors including cardiac arrest, obstruction in the airway, drug overdose, injury or diseases, seizures, holding their breath, gastroesophageal reflux (heartburn), cyanide poisoning, carbon monoxide poisoning, irregular heartbeat, stroke, etc. Many respiratory arrests are caused by choking, while some can also be caused by neurological disorders and muscular impairments. A person that has gone into a respiratory arrest should be provided cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) or artificial ventilation (if available). If respiratory is untreated for more than five minutes, the person has a higher change of dying.
Symptoms of respiratory arrest include: Cessation of breathing, cyanosis, progressive loss of consciousness, low blood oxygen levels. Treatment includes artificial respiration, CPR, medications (in case of a viral or bacterial infection) and surgery (if the heart requires it). Many people may require assisted breathing, if they are unable to breathe on their own. If treated effectively and in time, respiratory arrest is full reversible.
Image Courtesy: ece.uc.edu, caehealthcare.com









Add new comment