Difference between Plasma and Led TV
Key Difference: Plasma displays are developed using noble gases that are electrically heated to produce light. LED (Light emitting diode) TVs are still LCD TVs that replace the original LCD’s CCFL (Cold Cathode Fluorescent Lamp) technology with LED technology. LED backlight provides is that it extends the life span of the TV, has the ability to provide Jet black level same as Plasma displays, is thinner and lighter compared to Plasmas. However, plasmas provide a better image quality, a good picture color depth, excellent contrast ratio, better motion and are cheaper compared to LEDs.

Plasma displays are developed using noble gases that are electrically heated to produce light. Light emitting diodes (LED) are liquid crystal display (LCD) TVs with an LED backlighting technology. Plasmas are beneficial for displays greater than 40 inches. Plasmas are praised for producing good image quality, good picture color depth, excellent contrast ratio, and better motion.
A plasma display has tiny cells of noble gases (neon and xenon) and a small amount of mercury in compartmentalized spaces between two glass panels. The panels also have two electrodes between the glass panels, an address electrode and the display electrodes. In order to create the pixels, the address electrode and the display electrodes are charged, which then releases an electric current that flows through the cell. The charge stimulates the gas atoms in the cells to release ultraviolet photons. The photons interact with the phosphor material on the cell walls and give off light, creating a visible light photon. Each pixel has three subpixels, one coated with red, one with blue and one with green. By manipulating the intensity of the current, the system can produce hundreds of different combinations of the three colors and creates an image on the screen.
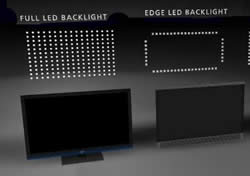 LED (Light emitting diode) TVs are still LCD TVs that replace the original LCD’s CCFL (Cold Cathode Fluorescent Lamp) technology with LED technology. An LED TV’s screen is also made up of liquid crystals. A LED is a semiconductor device and when it is switched on, electrons are able to recombine with electron holes within the device and release energy in form photons or light. This light emitted from an LED is used as a backlighting for an LCD TV. There are two forms in which and LED is used to light up an LCD; edge lighting and full array lighting.
LED (Light emitting diode) TVs are still LCD TVs that replace the original LCD’s CCFL (Cold Cathode Fluorescent Lamp) technology with LED technology. An LED TV’s screen is also made up of liquid crystals. A LED is a semiconductor device and when it is switched on, electrons are able to recombine with electron holes within the device and release energy in form photons or light. This light emitted from an LED is used as a backlighting for an LCD TV. There are two forms in which and LED is used to light up an LCD; edge lighting and full array lighting.
In edge lighting, a series of diodes are arranged along the outside edges of the screen, when a current is applied the light is then distributed evenly along the screen. This is similar to using CCFL lighting as it does not have local-dimming capabilities (where images are dimmed in response to their surroundings). In fully-array, the diodes are spread across the entire surface of the screen. These are faster in response and include the local-dimming feature as they have the capability of turning on and off independently.
A less confusing term for LED TV would be an LED-backlit LCD TV. A few benefits that an LED backlight provides is that it extends the life span of the TV, has the ability to provide Jet black level same as Plasma displays, is thinner and lighter compared to Plasmas. However, plasmas provide a better image quality, a good picture color depth, excellent contrast ratio, better motion and are cheaper compared to LEDs.
|
|
Plasma |
LED |
|
Thickness |
Minimum 3 inches |
Thinner compared to LCD |
|
Power consumption |
Consumes more power compared to LED |
Consumes less power than Plasma |
|
Screen Refresh Rate |
Slower compared to LED |
Greater than Plasma |
|
Screen glare |
More glare compared to LED |
Glare is minimum |
|
Running Temperature |
Hot |
Cool |
|
Burn-in |
Burn-in can occur with old displays |
No burn-in occurs; but burn-outs can occur |
|
Dead pixels |
Cannot occur |
Can occur |
|
Viewing angle |
Up to 160 degrees |
Up to 165 degrees |
|
Contrast Ratio |
3000:1 |
15000:1 |
|
Life span |
Modern plasmas have 60,000 hours |
100,000 hours |
|
Black level |
Jet Black |
Jet Black |
|
Weight |
Heavier compared to LED |
Lighter compared to Plasma |
|
Uses |
Computer monitors, TV screens |
Computer monitors, laptop screens, TV screens and cell phone screens |
|
Price |
Cheaper compared to LEDs |
More expensive |
|
Benefits |
Excellent contrast and black levels; effortless motion; good picture depth; Less visible motion blur; fast refresh rate |
Weight less than LCD; have a longer life; more environment friendly; lower power consumption; more reliable |
|
Limitations |
Not as power-efficient or thin as most LEDs; generates heat; susceptible to burn in and image retention; does not work well in high-altitudes |
Expensive |
Image Courtesy: howstuffworks.com, ledvslcd.com









Add new comment