Difference between Pinocytosis and Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
Key difference: Pinocytosis is essentially the process of absorbing fluid together with its contents into the cell. Receptor-mediated endocytosis (RME) is the process by which a cell absorbs nutrients into the cell via selective receptors on the cell membrane.
Both pinocytosis and receptor-mediated endocytosis are types of endocytosis. Endocytosis is a process by which cells absorb molecules by engulfing them. These molecules often include proteins and other substances which are important for the cell’s existence. The process of endocytosis is used by all cells as the molecules are large polar molecules that cannot pass through the hydrophobic plasma or cell membrane.
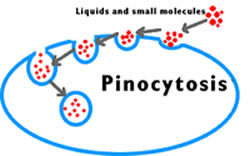
Pinocytosis is essentially the process of absorbing fluid together with its contents into the cell. The cell does this by forming narrow channels through its membrane. These channels surround the liquid and all its contents and then pinch off into vesicles, hence the liquid in successfully absorbed into the cell. The molecules then fuse with lysosomes to hydrolyze or be broken down. The process of pinocytosis requires a lot of energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate. This is the chemical compound that is generally used as energy in most cells.
Receptor-mediated endocytosis (RME) is the process by which a cell absorbs nutrients into the cell. The cell membrane is lined with receptors which seek their compatible nutrients or molecules. Once they find the nutrient, the receptors receive a signal through the membrane. The process then leads to a membrane coating. The receptors, now coated will now attach to the molecule. The plasma membrane will then surround the molecule, which will then be absorbed into the cell via a vesicle. The vesicle then abandons the nutrient and un-coats itself. It then returns to the cell membrane. The molecule or the nutrient is then fused with lysosomes to be hydrolyzed or be broken down.
 The function of RME is very diverse. Not only is it used for absorption of specific certain substances which are required by the cell, including but not limited to LDL or iron, via their specific receptors such as LDL receptor and transferrin, respectively. It is also used for downregulation of transmembrane signal transduction, which is essentially when the receptors become internalized and are transported to the late endosomes and lysosomes for degradation.
The function of RME is very diverse. Not only is it used for absorption of specific certain substances which are required by the cell, including but not limited to LDL or iron, via their specific receptors such as LDL receptor and transferrin, respectively. It is also used for downregulation of transmembrane signal transduction, which is essentially when the receptors become internalized and are transported to the late endosomes and lysosomes for degradation.
It has also been implied by scientists that RME is also actively involved in transducing signals from the cell periphery to the nucleus. This is implied as the association and formation of specific signaling complexes is required for the effective signaling of hormones, such as EGF.
The main difference between pinocytosis and RME is that, pinocytosis is the absorption of liquids, whereas receptor-mediated endocytosis absorbs certain specific nutrient as required by the cell. Also, unlike pinocytosis, RME is a much selective process, where the receptors will only target the nutrient with which they are compatible and none other. RME is also called clathrin-dependent endocytosis.
Image Courtesy: science.halleyhosting.com, jedismedicine.blogspot.in








Add new comment